Building a mezzanine? Sounds simple, right? Think again! Getting the height wrong can be a real headache – costly delays, safety problems, and even legal trouble. This guide cuts through the confusion around mezzanine floor heights, showing you exactly what you need to know to meet all the rules and regulations. We’ll explain the key things to watch out for, why getting the height right is so important for safety, and give you practical tips to design your mezzanine correctly. We’ll even show you the differences between the major building codes so you don’t get caught out. By the end, you’ll be confident you’re building a safe and compliant mezzanine, saving yourself time, money, and stress. For more on structural integrity, check out this guide on mezzanine load capacity.
Mezzanine Height Regulations and Safety Protocols
Building a mezzanine is a fantastic way to maximize space, but it’s essential to get the height right. This isn’t just about aesthetics; it’s about safety, legality, and avoiding costly headaches later. This guide breaks down everything you need to know to build a compliant and safe mezzanine, considering important factors like structural integrity, fire safety, and legal compliance.
Decoding Height Requirements: IBC, OSHA, and Compliance
The International Building Code (IBC) and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) are the primary regulatory bodies. Understanding their requirements is key to a successful project. The IBC typically requires a minimum of seven feet of clear headroom both above and below your mezzanine. This isn’t arbitrary; it’s a critical safety measure, ensuring comfortable movement and preventing head injuries, promoting safe passage and preventing workplace accidents.
OSHA also plays a crucial role, focusing primarily on worker safety during construction and use, emphasizing occupational safety. They have specific rules concerning fall protection, regardless of whether your mezzanine meets the IBC’s height standards. Consider this: the IBC establishes minimum structural requirements, while OSHA emphasizes the safety of those using the structure, ensuring regulatory adherence and preventing penalties.
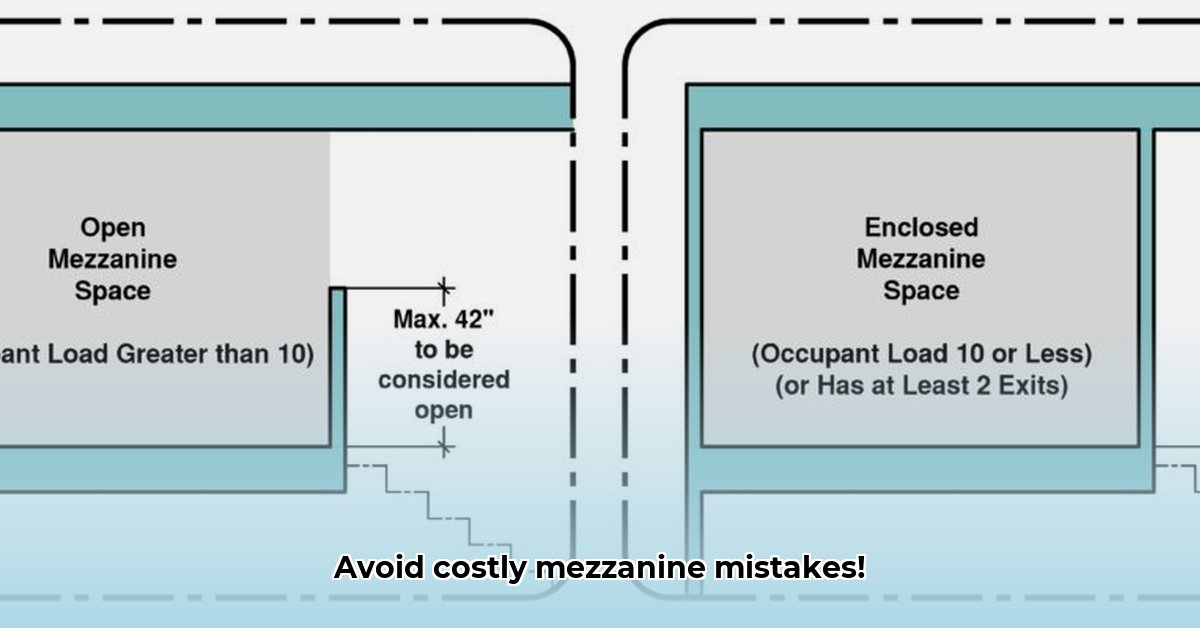
Area Limitations, Access Points, and Other Considerations
The IBC often limits a mezzanine’s size to one-third of the floor area below. This is primarily a fire safety measure, facilitating easier evacuation in emergencies, promoting hazard mitigation. Exceptions exist, however. If you have a specialized building type or an advanced fire suppression system, you might be able to construct a larger mezzanine. Always consult with your local building department to confirm applicable regulations.
Access to your mezzanine is as critical as its height and size. Building codes generally require multiple, safe, and convenient exits – essentially, a well-planned escape strategy. The goal is to ensure occupants aren’t trapped with only one way out. Multiple exits are a crucial safety feature.
The Defining Role of Local Building Regulations
Building codes aren’t uniform nationwide. Your local jurisdiction (town, city, or county) may have supplemental rules and regulations beyond the national IBC and OSHA standards. This means your neighbor’s mezzanine requirements could differ from yours. The only way to be certain is to consult with your local building department before commencing any work – the only way to ensure full compliance with zoning ordinances and avoid legal issues.
Step-by-Step Guide to a Compliant Mezzanine Floor
Constructing a code-compliant mezzanine is a comprehensive process. Here’s a helpful step-by-step guide:
- Know Your Site: Conduct a thorough assessment of your space. Identify existing structures, utilities, and any limitations of the available area. This initial assessment is crucial for effective spatial planning.
- Code Deep Dive: Consult the IBC, OSHA guidelines, and your local building department’s requirements. Understanding the specific rules for your area is essential, ensuring regulation compliance and preventing project delays.
- Professional Expertise: Engage a qualified architect or structural engineer. They specialize in navigating these regulations and can design your mezzanine to meet all codes and ensure structural soundness. This upfront investment provides peace of mind, ensuring structural integrity and code compliance.
- Permitting Process: Obtain all necessary permits and approvals before starting construction. This is a legal requirement and will prevent delays and potential problems down the line, ensuring legal authorization.
- Construction Phase: Strictly adhere to approved blueprints during construction and ensure your contractor complies with all safety regulations, particularly OSHA’s requirements, prioritizing worker protection. Regular site visits are recommended.
- Inspections: Schedule regular inspections throughout construction and after completion. This ensures code compliance and allows for early detection and correction of any issues, paying close attention to fall protection and the overall structural integrity of the mezzanine, ensuring safety standards and regulatory adherence.
Team Effort: Sharing Responsibility for Mezzanine Safety
A successful mezzanine project requires collaboration between all stakeholders, with each playing a vital role in ensuring a safe and compliant structure.
| Stakeholder | Key Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Building Owners/Managers | Site assessment, code review, securing permits, ongoing maintenance, with a focus on risk management. |
| Architects/Engineers | Design compliance, detailed blueprints, material specification, overseeing construction, ensuring design accuracy. |
| Contractors | Adhering to plans, worker safety, meeting safety standards, delivering a quality product, maintaining quality control. |
| Local Authorities | Enforcing building codes, reviewing permits, clear communication of regulations, ensuring regulation enforcement. |
Avoiding Costly Construction Oversights
Cutting corners regarding mezzanine height requirements can lead to significant expenses, including potential delays, fines, and legal action. Safety is paramount and mandated by law.
A poorly planned or constructed mezzanine is a potential hazard. Investing in quality design and professional expertise will save money and prevent problems, promoting proactive compliance. Don’t compromise on safety; it’s an investment, not an expense.
Mezzanine Construction: OSHA and IBC Compliance Considerations
Key Takeaways:
- Mezzanine installation necessitates careful consideration of International Building Code (IBC), Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) regulations, and local codes.
- Understanding minimum height clearances, maximum area restrictions, and egress requirements is crucial for compliance and risk mitigation.
- Thorough planning, precise documentation, and effective communication with authorities are essential for project success and prevent regulatory interventions.
- Variances may be necessary for projects exceeding standard code limitations, requiring skillful navigation of the permitting process.
- Seismic zone requirements and fire codes significantly influence design and necessitate collaboration with local fire departments.
- Careful integration of IBC egress requirements and OSHA fall protection regulations is paramount throughout design and construction.
- The mezzanine type influences permitting and construction, affecting project timelines. Careful planning minimizes delays and issues.
Understanding the Regulations for Mezzanine Development
Building a mezzanine involves navigating a complex regulatory landscape. The International Building Code (IBC) establishes national standards, but local jurisdictions often impose additional requirements. A key question is how to ensure OSHA and IBC compliance for mezzanine construction in varying local jurisdictions. OSHA’s regulations focus on worker safety. Ignoring these codes can result in substantial fines and legal repercussions. Understanding these regulations can ensure liability protection and project success.
Step-by-Step Guide to Compliance for Mezzanines
- Initial Assessment: Begin with a comprehensive site survey, including measurements, structural capacity assessment, and identification of existing utilities. Note any regional concerns related to environmental factors.
- Code Research: Determine the specific IBC and OSHA requirements applicable to your area. Local building departments are invaluable resources for obtaining expert guidance.
- Design & Engineering: Engage a qualified structural engineer to design your mezzanine. The design must comply with all applicable building codes, including proper materials, sufficient load capacity, and adherence to height and area requirements, ensuring design accuracy.
- Permitting: Submit complete plans and documentation to local authorities, understanding the exact requirements, which often include drawings, calculations, and specifications, streamlining the approval process.
- Construction: Engage a licensed and insured contractor experienced in mezzanine construction, maintaining detailed construction logs and prioritizing safe work practices. Ensure adequate workforce training.
- Inspection: Facilitate regular inspections by building officials throughout construction, addressing any compliance issues promptly, ensuring quality assurance.
- Post-Construction: Obtain necessary certificates of occupancy upon completion and maintain records of the structure’s load capacity.
Height Requirements and Clearance Considerations
Mezzanine height requirements are critical. The IBC generally mandates a minimum 7-foot clearance under the mezzanine and a similar clearance above it. These are
- Glass Tile Shower Ideas to Create a Stunning Bathroom Space - December 7, 2025
- Glass Wall Tile Ideas for Kitchens and Bathrooms - December 6, 2025
- Glass Tile Bathroom: Create a Beautiful, Easy-Clean Space - December 5, 2025